An electrician could be working in one moment, and in the next, there’s an explosion. As you probably know, electrical work is dangerous, especially with large voltages and currents that may cause arc flashes.
Understanding what causes arc flashes helps anyone working with electrical systems to avoid them. This guide will explore key arc flash risks electricians face and provide actionable ways to stay safe on the job. Benchmark ESS’s training programs are geared toward providing a secure workplace.
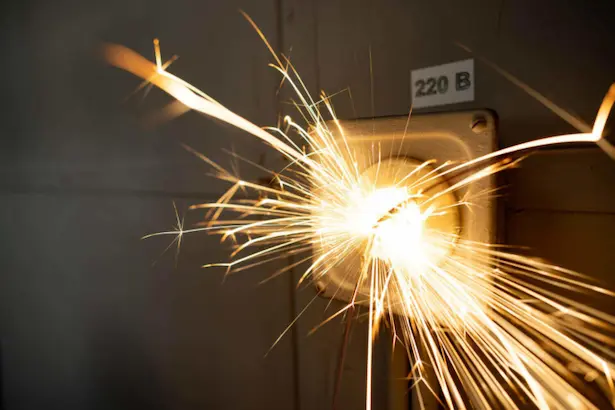

The Dangers of Electrical Arc Flash
Arc flashes are significant hazardous risks for electricians. When they happen, the results are violently dangerous. Temperatures can spike up to 35,000°F, the same heat as the sun’s surface. This extreme heat vaporizes metal parts and causes severe skin burns to those close by.
The pressure wave also packs enough force to throw workers across rooms or knock them off ladders. Further, UV radiation emissions are harmful to the eyes. Full-on arc blasts account for many electrical worker deaths and life-altering injuries each year.
While nothing eliminates arc hazards, understanding the causes empowers electricians to take preventative steps. Common triggers include dust or impurities between high-voltage connections. Other triggers are corrosion, equipment failures, dropped tools, and accidental touching of live parts. They recognize these red flags and work cautiously around risky setups to safeguard electricians against arc flashes.
Vital Protective Measures
Workplace safety regulations require certain precautions in any environment with electrical arc flash risks. Compliance protects both workers and companies from hazards. Key protections include:
- Insulated Tools and Equipment
- Arc flash-resistant PPE
- Established Safety Protocols
- Proper Training
Using insulated, arc-rated tools and equipment is the first barrier against live electric parts. Special arc flash suits and fire-retardant clothing also reduce potential burn impacts. Moreover, strict protocols minimize accidental activations near energized equipment. More importantly, proper training ensures everyone recognizes arc dangers and knows how to avoid them.
Let’s explore comprehensive arc injury avoidance in more detail.
Reducing Electrical Arc Flash Hazards

Looking at a few situations helps highlight the multifaceted approach needed to secure arc flash safety:
Scenario #1
An electrician suffered severe burns on over 40% of his body due to an arc blast while working inside a 480V panel. The direct cause was dust buildup, allowing arc propagation between bus bars upon re-energization after repairs.
To prevent future occurrences, the company implements a stricter panel cleaning protocol. They also mandate de-energized states for interior work per safety codes. Further, electricians now wear arc-rated suits for added protection in case of incidents.
Scenario #2
An apprentice electrician narrowly avoided injury when an improperly insulated screwdriver slipped while working near a live conductor. Luckily, their mentor noticed the slip in time to quickly flip the disconnect switch.
The company reinforces bans on uninsulated tools. They also amend daily start-up meetings to include arc hazard checks. This fast recognition resolved a dangerous situation. Strengthening safety protocols and proper tool requirements aims to prevent close calls.
Scenario #3
An electrician was inspecting a new equipment installation and accidentally brushed their elbow against an adjacent live bus while reaching inside the cabinet. That resulted in an arc that caused flash burns that required hospitalization.
In response, updated procedures demand full de-energization for any internal equipment access. Arc flash PPE also became mandatory for de-energized work. This avoidable incident would not have happened if proper protocols and gear had been used initially.
These examples showcase the value of layered electrical safety methods. Keeping gear properly insulated g, following strict access protocols, wearing arc-rated PPE, and maintaining vigilance lowers risks. Bufully securing worksites also requires another critical element.
The Critical Role of Electrical Arc Flash Safety Training
Most vital of all is proper workforce education on electrical hazards. Training specific to arc dangers teaches electricians critical skills. These include:
- Identifying Arc Flash Risks: Spotting hazards lets workers approach cautiously.
- Using PPE: Learning standards for protective gear and proper wear prevents injury.
- Checking Safety Systems: Testing tools and backup measures increase reliability.
- Navigating Safety Protocols: Understanding and adhering to procedures avoids incidents.
- Responding to Arc Events: Knowing how to react quickly reduces harm.
Consistent education paired with equipment inspections and maintenance fosters an informed, safety-focused environment. This culture of awareness offers the best defense.
Seeking a Higher Standard Through Arc Flash Hazard Analysis
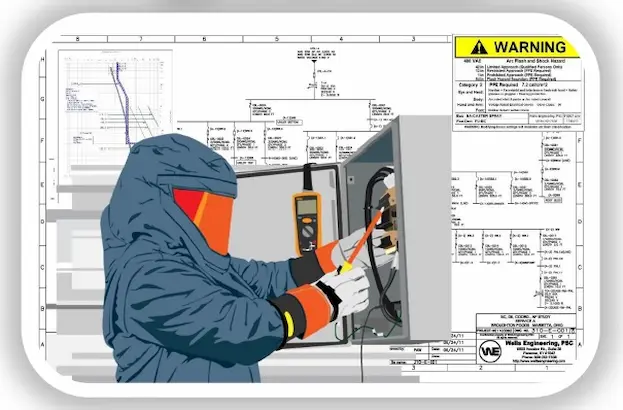
Performing Arc Flash Hazard Analysis (AFHA) for companies serious about safety can further reduce risk. This systematic process uses advanced analytical tools to examine a facility’s electrical infrastructure. It determines available incident energy levels for arc faults at various locations.
The analysis outputs critical data like flash protection boundaries, hazard risk categories, PPE requirements, and safety protocols. Facility managers then integrate these findings into infrastructure designs, operating procedures, worker training, equipment signage, and arc incident response plans.
Trusting a Safety-Focused Service Provider
Not all electrical contractors prioritize safety with the same commitment. Facility managers should select only arc flash safety-focused providers when choosing commercial work partners.
By selecting electrical arc flash safety trailblazers for electrical projects, companies are ready for incidents-free work environments.
Conclusion: A Shared Responsibility
In electrical systems, arc hazards pose an ever-present risk. Yet, these threats can be minimized through shared diligence across contractors, businesses, and workers. Ultimately, arc safety relies on strategic equipment use, strict preventative actions, advanced training, and conscientious workers.